import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mikeio
import mikeio.genericConcatenation
Generic
The generic module contains functionality that works for all types of dfs (dfs0, dfs1, dfs2, dfs3, dfsu) files:
concat()- Concatenates files along the time axisextract()- Extract timesteps and/or items to a new dfs filediff()- Calculate difference between two dfs files with identical geometryadd()- Calculate the sum of two dfs filesscale()- Apply scaling to any dfs fileavg_time()- Create a temporally averaged dfs filequantile()- Create a dfs file with temporal quantilestransform()- Create new derived items from existing items using custom functions
When to use the generic module
- The processing is not tied to the spatial dimension of the data
- When the files are large and you want to avoid reading the entire file into memory
When not to use the generic module
- When you need processing depending on the spatial information in the file. For example, spatial interpolation, subsetting, etc.
- When you need more complex processing, not covered by the generic module
- When the input files data are not dfs files
- When the end result is not a dfs file
Examples
Take a look at these two files with overlapping timesteps.
t1 = mikeio.read("../data/tide1.dfs1")
t1<mikeio.Dataset>
dims: (time:97, x:10)
time: 2019-01-01 00:00:00 - 2019-01-03 00:00:00 (97 records)
geometry: Grid1D (n=10, dx=0.06667)
items:
0: Level <Water Level> (meter)t2 = mikeio.read("../data/tide2.dfs1")
t2<mikeio.Dataset>
dims: (time:97, x:10)
time: 2019-01-02 00:00:00 - 2019-01-04 00:00:00 (97 records)
geometry: Grid1D (n=10, dx=0.06667)
items:
0: Level <Water Level> (meter)Plot one of the points along the line.
plt.plot(t1.time,t1[0].isel(x=1).values, label="File 1")
plt.plot(t2.time,t2[0].isel(x=1).values,'k+', label="File 2")
plt.legend()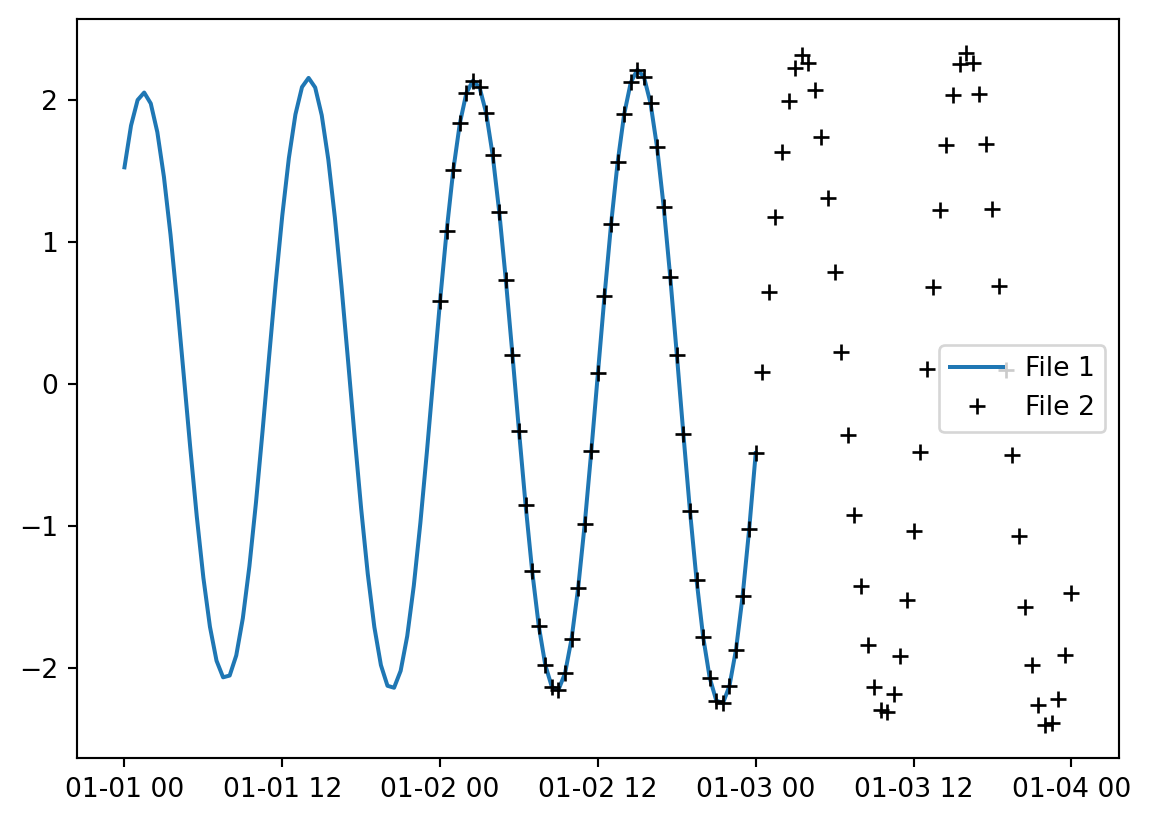
mikeio.generic.concat(infilenames=["../data/tide1.dfs1",
"../data/tide2.dfs1"],
outfilename="concat.dfs1") 0%| | 0/2 [00:00<?, ?it/s]100%|██████████| 2/2 [00:00<00:00, 755.53it/s]c = mikeio.read("concat.dfs1")
c[0].isel(x=1).plot()
c<mikeio.Dataset>
dims: (time:145, x:10)
time: 2019-01-01 00:00:00 - 2019-01-04 00:00:00 (145 records)
geometry: Grid1D (n=10, dx=0.06667)
items:
0: Level <Water Level> (meter)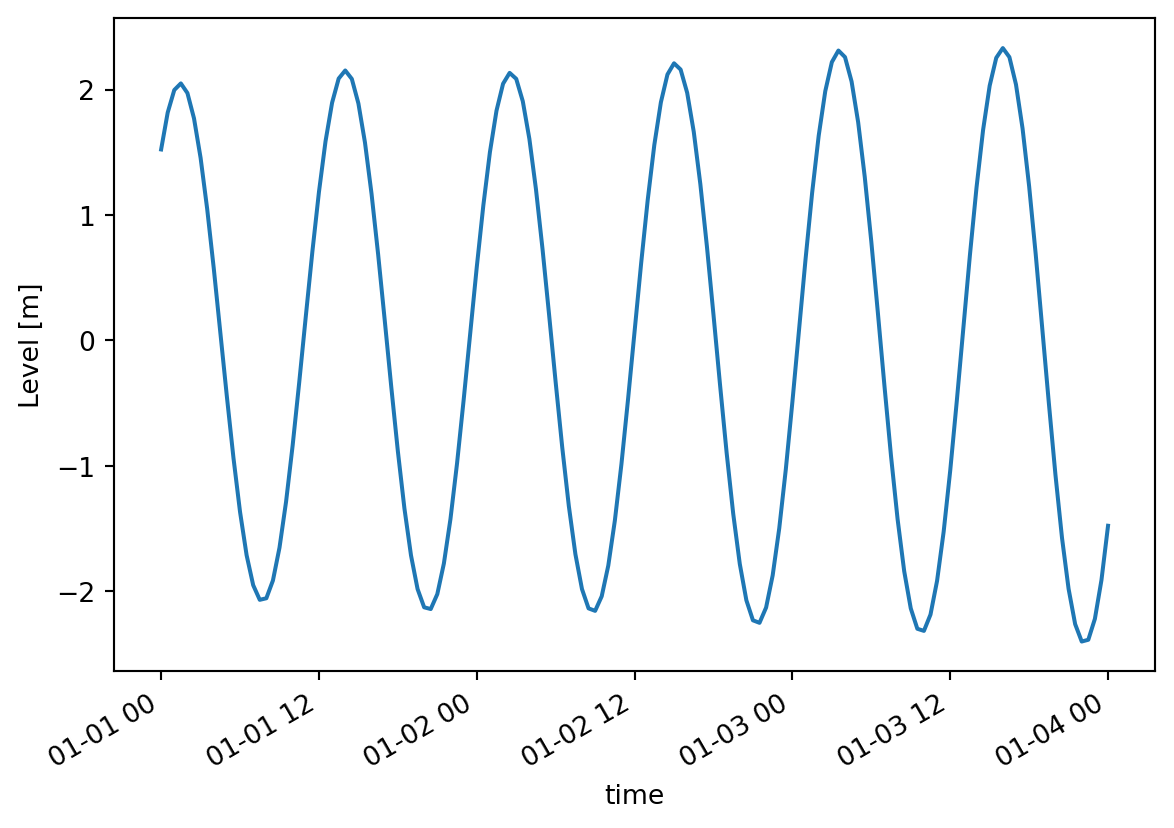
Difference between two files
Take difference between two dfs files with same structure - e.g. to see the difference in result between two calibration runs
fn1 = "../data/oresundHD_run1.dfsu"
fn2 = "../data/oresundHD_run2.dfsu"
fn_diff = "oresundHD_difference.dfsu"
mikeio.generic.diff(fn1, fn2, fn_diff) 0%| | 0/5 [00:00<?, ?it/s]100%|██████████| 5/5 [00:00<00:00, 2844.75it/s]_, ax = plt.subplots(1,3, sharey=True, figsize=(12,5))
da = mikeio.read(fn1, time=-1)[0]
da.plot(vmin=0.06, vmax=0.27, ax=ax[0], title='run 1')
da = mikeio.read(fn2, time=-1)[0]
da.plot(vmin=0.06, vmax=0.27, ax=ax[1], title='run 2')
da = mikeio.read(fn_diff, time=-1)[0]
da.plot(vmin=-0.1, vmax=0.1, cmap='coolwarm', ax=ax[2], title='difference');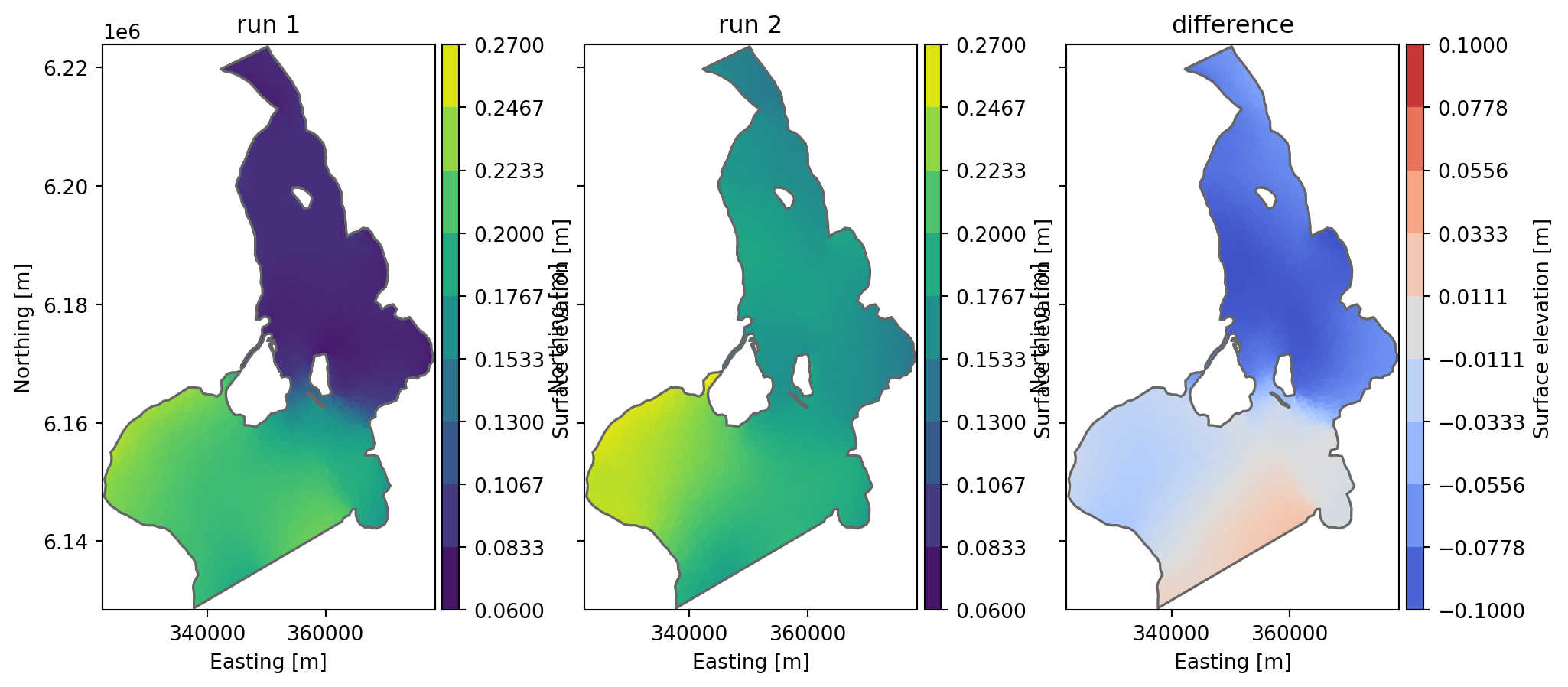
Extract time steps or items
The extract() method can extract a part of a file:
- time slice by specifying start and/or end
- specific items
mikeio.generic.extract("../data/tide1.dfs1", "extracted.dfs1", start="2019-01-02")e = mikeio.read("extracted.dfs1")
e<mikeio.Dataset>
dims: (time:49, x:10)
time: 2019-01-02 00:00:00 - 2019-01-03 00:00:00 (49 records)
geometry: Grid1D (n=10, dx=0.06667)
items:
0: Level <Water Level> (meter)mikeio.generic.extract(
"../data/oresund_vertical_slice.dfsu", "extracted.dfsu", items="Salinity", end=-2
)e = mikeio.read("extracted.dfsu")
e<mikeio.Dataset>
dims: (time:2, element:441)
time: 1997-09-15 21:00:00 - 1997-09-16 00:00:00 (2 records)
geometry: DfsuVerticalProfileSigmaZ (441 elements, 550 nodes)
items:
0: Salinity <Salinity> (PSU)Scaling
Adding a constant e.g to adjust datum
ds = mikeio.read("../data/gebco_sound.dfs2")
ds.Elevation[0].plot();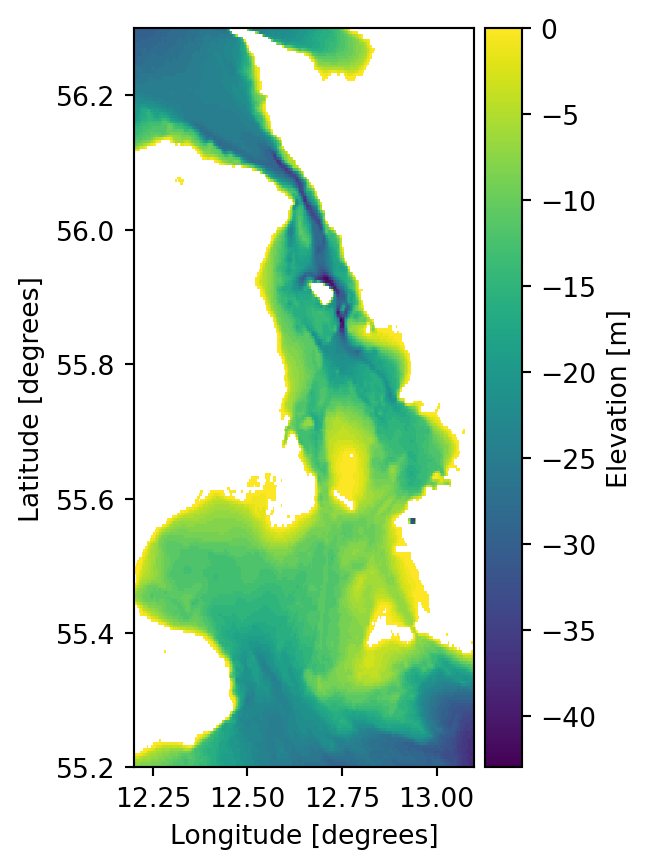
ds['Elevation'][0,104,131].to_numpy()np.float32(-1.0)This is the processing step.
mikeio.generic.scale("../data/gebco_sound.dfs2",
"gebco_sound_local_datum.dfs2",
offset=-2.1
) 0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?it/s]100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1272.54it/s]ds2 = mikeio.read("gebco_sound_local_datum.dfs2")
ds2['Elevation'][0].plot()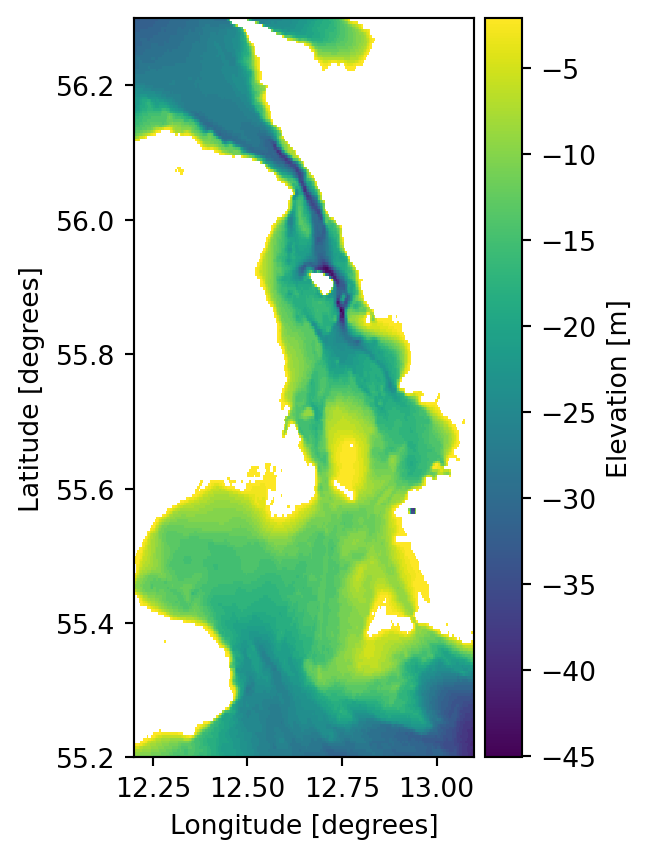
ds2['Elevation'][0,104,131].to_numpy()np.float32(-3.1)Spatially varying correction
factor = np.ones_like(ds['Elevation'][0].to_numpy())
factor.shape(264, 216)Add some spatially varying factors, exaggerated values for educational purpose.
factor[:,0:100] = 5.3
factor[0:40,] = 0.1
factor[150:,150:] = 10.7
plt.imshow(factor)
plt.colorbar();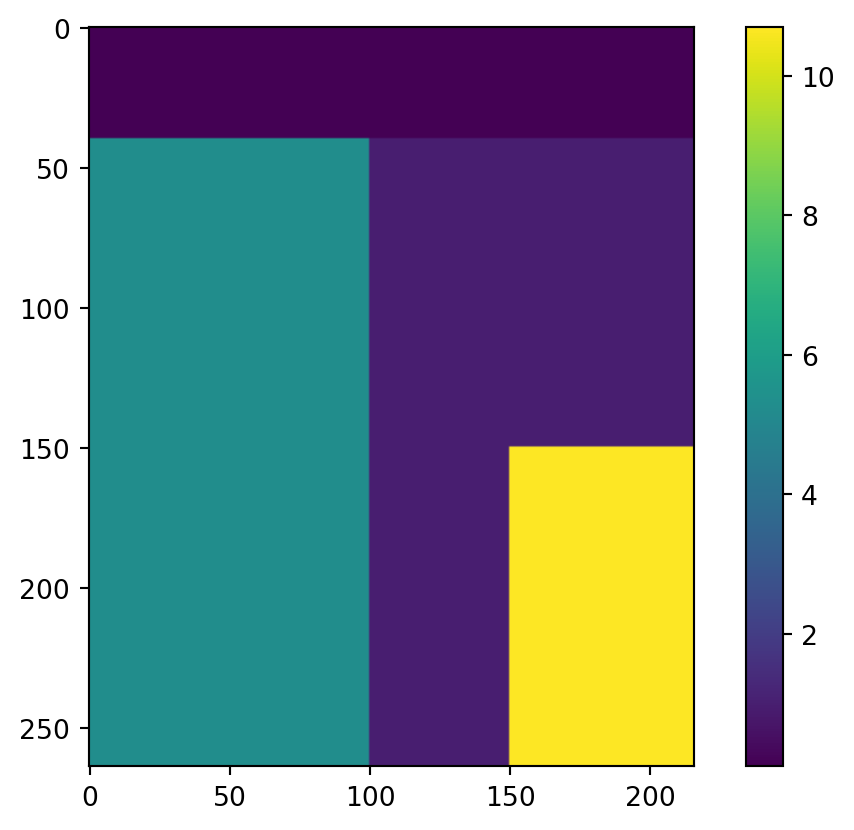
The 2d array must first be flipped upside down and then converted to a 1d vector using numpy.ndarray.flatten to match how data is stored in dfs files.
factor_ud = np.flipud(factor)
factor_vec = factor_ud.flatten()
mikeio.generic.scale("../data/gebco_sound.dfs2",
"gebco_sound_spatial.dfs2",
factor=factor_vec
) 0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?it/s]100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1239.82it/s]ds3 = mikeio.read("gebco_sound_spatial.dfs2")
ds3.Elevation[0].plot();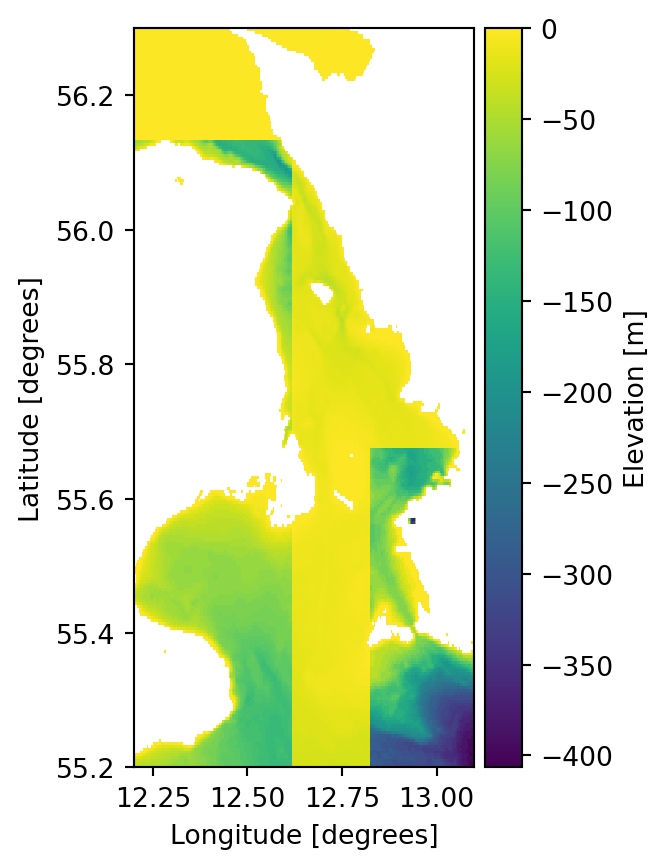
Derived items
Creating derived items from existing items, e.g. current speed from u and v velocities.
from mikeio.generic import DerivedItem
mikeio.generic.transform(
infilename="../data/oresundHD_run1.dfsu",
outfilename="oresundHD_speed.dfsu",
vars=[
DerivedItem(
name="Current speed",
type=mikeio.EUMType.Current_Speed,
unit=mikeio.EUMUnit.knot,
func=lambda x: 1.94 * np.sqrt(x["U velocity"] ** 2 + x["V velocity"] ** 2),
)
],
)Time average
mikeio.generic.avg_time(
"../data/NorthSea_HD_and_windspeed.dfsu", "Avg_NorthSea_HD_and_windspeed.dfsu"
) 0%| | 0/66 [00:00<?, ?it/s]100%|██████████| 66/66 [00:00<00:00, 24966.10it/s]ds = mikeio.read("../data/NorthSea_HD_and_windspeed.dfsu")
ds.mean(axis=0).describe() # alternative way of getting the time average| Surface elevation | Wind speed | |
|---|---|---|
| count | 958.000000 | 958.000000 |
| mean | 0.449857 | 12.772706 |
| std | 0.178127 | 2.367667 |
| min | 0.114355 | 6.498364 |
| 25% | 0.373691 | 11.199439 |
| 50% | 0.431747 | 12.984060 |
| 75% | 0.479224 | 14.658077 |
| max | 1.202888 | 16.677952 |
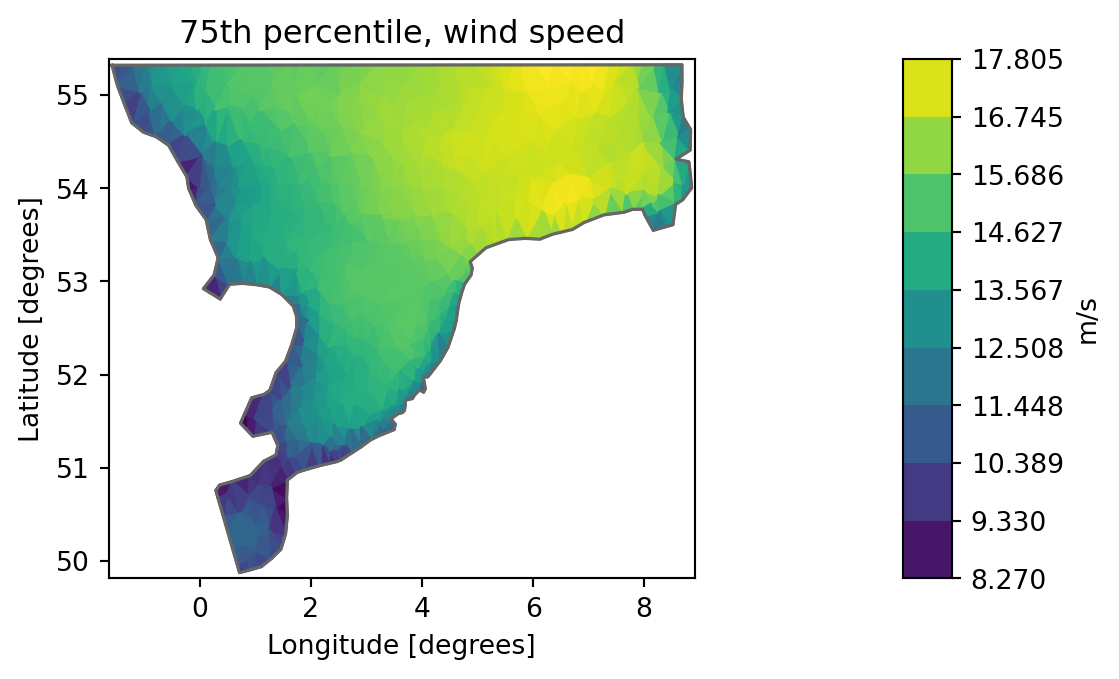
Quantile
Example that calculates the 25%, 50% and 75% percentile for all items in a dfsu file.
fn = "../data/NorthSea_HD_and_windspeed.dfsu"
fn_q = "Q_NorthSea_HD_and_windspeed.dfsu"
mikeio.generic.quantile(fn, fn_q, q=[0.25,0.5,0.75])ds = mikeio.read(fn_q)
ds<mikeio.Dataset>
dims: (time:1, element:958)
time: 2017-10-27 00:00:00 (time-invariant)
geometry: Dfsu2D (958 elements, 570 nodes)
items:
0: Quantile 0.25, Surface elevation <Surface Elevation> (meter)
1: Quantile 0.5, Surface elevation <Surface Elevation> (meter)
2: Quantile 0.75, Surface elevation <Surface Elevation> (meter)
3: Quantile 0.25, Wind speed <Wind speed> (meter per sec)
4: Quantile 0.5, Wind speed <Wind speed> (meter per sec)
5: Quantile 0.75, Wind speed <Wind speed> (meter per sec)da_q75 = ds["Quantile 0.75, Wind speed"]
da_q75.plot(title="75th percentile, wind speed", label="m/s")