Generic dfs processing#
Tools and methods that applies to any type of dfs files.
The generic tools are useful for common data processing tasks, where detailed configuration is not necessary.
mikeio.generic: methods that read any dfs file and outputs a new dfs file of the same type
concat: Concatenates files along the time axis
scale: Apply scaling to any dfs file
sum: Sum two dfs files
diff: Calculate difference between two dfs files
extract: Extract timesteps and/or items to a new dfs file
time-avg: Create a temporally averaged dfs file
quantile: Create temporal quantiles of dfs file
The generic methods works on larger-than-memory files as they process one time step at a time. This can however make them in-efficient for dfs0 processing!
See Generic in MIKE IO Documentation
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mikeio
import mikeio.generic
Concatenation#
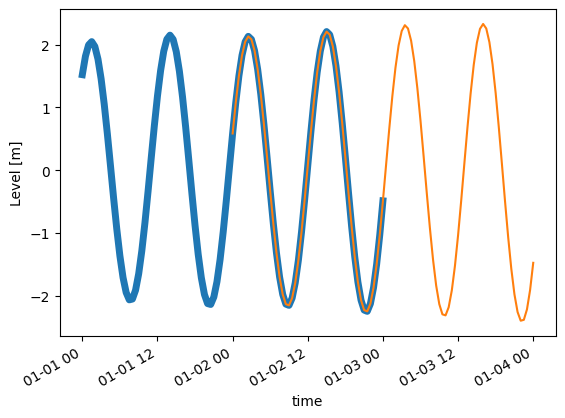
Take a look at these two files with overlapping timesteps.
t1 = mikeio.read("data/tide1.dfs1")
t1
<mikeio.Dataset>
dims: (time:97, x:10)
time: 2019-01-01 00:00:00 - 2019-01-03 00:00:00 (97 records)
geometry: Grid1D (n=10, dx=0.06667)
items:
0: Level <Water Level> (meter)
t2 = mikeio.read("data/tide2.dfs1")
t2
<mikeio.Dataset>
dims: (time:97, x:10)
time: 2019-01-02 00:00:00 - 2019-01-04 00:00:00 (97 records)
geometry: Grid1D (n=10, dx=0.06667)
items:
0: Level <Water Level> (meter)
Plot one of the points along the line.
ax = t1[0].isel(x=1).plot(lw=5)
t2[0].isel(x=1).plot(ax=ax);
mikeio.generic.concat(infilenames=["data/tide1.dfs1",
"data/tide2.dfs1"],
outfilename="concat.dfs1")
0%| | 0/2 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
100%|██████████| 2/2 [00:00<00:00, 651.44it/s]
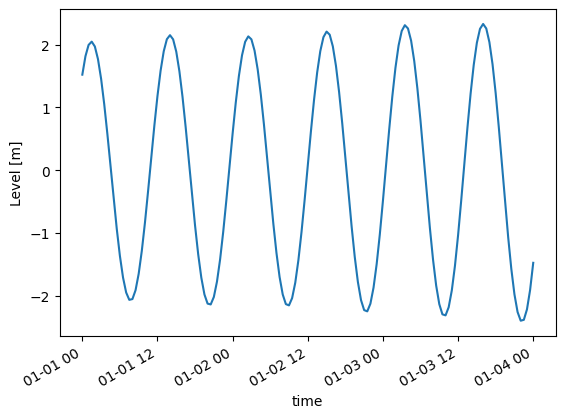
c = mikeio.read("concat.dfs1")
c
<mikeio.Dataset>
dims: (time:145, x:10)
time: 2019-01-01 00:00:00 - 2019-01-04 00:00:00 (145 records)
geometry: Grid1D (n=10, dx=0.06667)
items:
0: Level <Water Level> (meter)
c[0].isel(x=1).plot();
Extract time steps or items#
The extract() method can extract a part of a file:
time slice by specifying start and/or end
specific items
infile = "data/tide1.dfs1"
mikeio.generic.extract(infile, "extracted.dfs1", start='2019-01-02')
e = mikeio.read("extracted.dfs1")
e
<mikeio.Dataset>
dims: (time:49, x:10)
time: 2019-01-02 00:00:00 - 2019-01-03 00:00:00 (49 records)
geometry: Grid1D (n=10, dx=0.06667)
items:
0: Level <Water Level> (meter)
infile = "data/oresund_vertical_slice.dfsu"
mikeio.generic.extract(infile, "extracted.dfsu", items='Salinity', end=-2)
e = mikeio.read("extracted.dfsu")
e
<mikeio.Dataset>
dims: (time:2, element:441)
time: 1997-09-15 21:00:00 - 1997-09-16 00:00:00 (2 records)
geometry: DfsuVerticalProfileSigmaZ (441 elements, 550 nodes)
items:
0: Salinity <Salinity> (PSU)
Inline exercise
use
mikeio.generic.extractto extract the data from the beginning of the file ‘data/tide2.dfs1’ until “2019-01-03”, into a new file named ‘tide_start.dfs1’use
mikeio.readto read the new file ‘tide_start.dfs1’ into a Dataset named dsCheck that the end time,
ds.end_timematches what you specified above
mikeio.read("data/tide2.dfs1")
<mikeio.Dataset>
dims: (time:97, x:10)
time: 2019-01-02 00:00:00 - 2019-01-04 00:00:00 (97 records)
geometry: Grid1D (n=10, dx=0.06667)
items:
0: Level <Water Level> (meter)
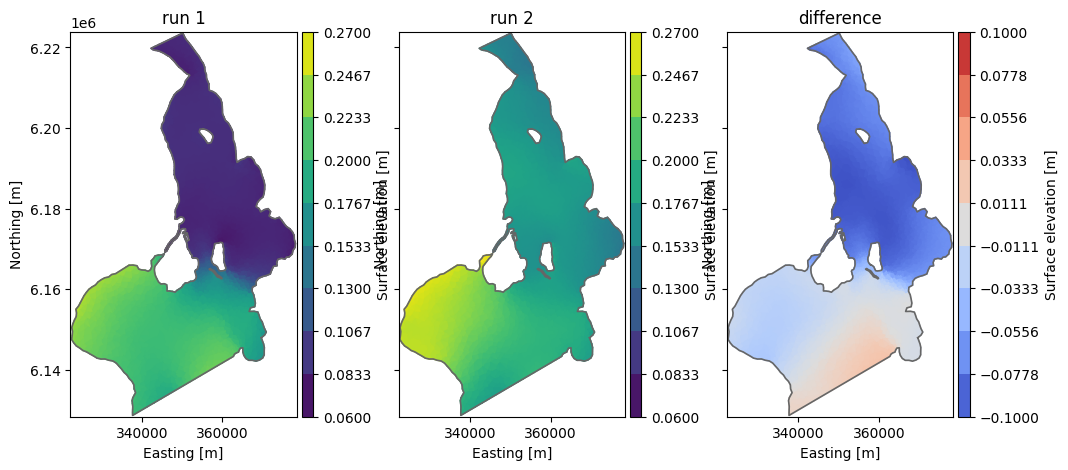
Diff#
Take difference between two dfs files with same structure - e.g. to see the difference in result between two calibration runs
fn1 = "data/oresundHD_run1.dfsu"
fn2 = "data/oresundHD_run2.dfsu"
fn_diff = "oresundHD_difference.dfsu"
mikeio.generic.diff(fn1, fn2, fn_diff)
0%| | 0/5 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
100%|██████████| 5/5 [00:00<00:00, 2899.42it/s]
Let’s open the files and visualize the last time step of the first item (water level)
_, ax = plt.subplots(1,3, sharey=True, figsize=(12,5))
da = mikeio.read(fn1, time=-1)[0]
da.plot(vmin=0.06, vmax=0.27, ax=ax[0], title='run 1')
da = mikeio.read(fn2, time=-1)[0]
da.plot(vmin=0.06, vmax=0.27, ax=ax[1], title='run 2')
da = mikeio.read(fn_diff, time=-1)[0]
da.plot(vmin=-0.1, vmax=0.1, cmap='coolwarm', ax=ax[2], title='difference');
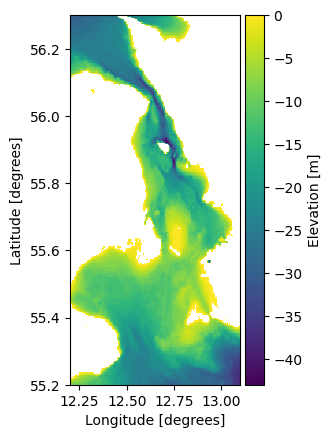
Scaling#
Adding a constant e.g to adjust datum
ds = mikeio.read("data/gebco_sound.dfs2")
ds.Elevation.plot();
ds['Elevation'][0,104,131]
<mikeio.DataArray>
name: Elevation
dims: ()
time: 2020-05-15 11:04:52 (time-invariant)
geometry: GeometryPoint2D(x=12.74791669513408, y=55.63541668926675)
values: -1.0
This is the processing step.
mikeio.generic.scale("data/gebco_sound.dfs2","gebco_sound_local_datum.dfs2",offset=-2.1)
0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1043.88it/s]
ds2 = mikeio.read("gebco_sound_local_datum.dfs2")
ds.Elevation.plot();

ds2['Elevation'][0,104,131]
<mikeio.DataArray>
name: Elevation
dims: ()
time: 2020-05-15 11:04:52 (time-invariant)
geometry: GeometryPoint2D(x=12.74791669513408, y=55.63541668926675)
values: -3.0999999046325684
Spatially varying correction#
import numpy as np
factor = np.ones_like(ds['Elevation'][0].to_numpy())
factor.shape
(264, 216)
Add some spatially varying factors, exaggerated values for educational purpose.
factor[:,0:100] = 5.3
factor[0:40,] = 0.1
factor[150:,150:] = 10.7
plt.imshow(factor)
plt.colorbar();
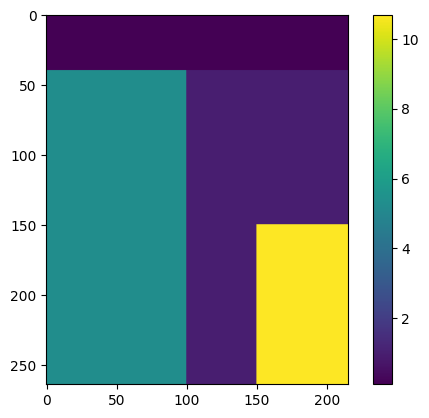
The 2d array must first be flipped upside down and then converted to a 1d vector using numpy.ndarray.flatten to match how data is stored in dfs files.
factor_ud = np.flipud(factor)
factor_vec = factor_ud.flatten()
mikeio.generic.scale("data/gebco_sound.dfs2","gebco_sound_spatial.dfs2",factor=factor_vec)
0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1204.57it/s]
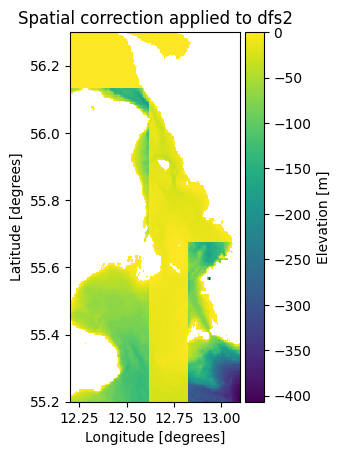
ds3 = mikeio.read("gebco_sound_spatial.dfs2")
ds3.Elevation.plot()
plt.title("Spatial correction applied to dfs2");
Clean up#
import os
os.remove("concat.dfs1")
os.remove("extracted.dfs1")
os.remove("extracted.dfsu")
os.remove("oresundHD_difference.dfsu")
os.remove("gebco_sound_local_datum.dfs2")
os.remove("gebco_sound_spatial.dfs2")
import utils
utils.sysinfo()
System: 3.11.14 (main, Oct 10 2025, 01:03:14) [GCC 13.3.0]
NumPy: 2.4.2
Pandas: 3.0.1
MIKE IO: 3.0.1
Last modified: 2026-03-05 10:03:30.251661

