Export to file#
A need for exporting dfsu files to other formats, such as raster formats (NetCDF, GeoTIFF) or vector formats (ESRI Shape, GeoJSON) are not uncommon.
There are usually very specific requirements about the exported data, naming, metadata, resolution and so on, which is why we don’t provide out of the box tools to convert files back and forth from a lot of formats, but instead provide the necessary building blocks and some examples to use as inspiration.
Examples#
Export to shapefile#
import mikeio
import geopandas as gpd
dfs = mikeio.open("data/oresundHD_run1.dfsu")
dfs
<mikeio.Dfsu2DH>
number of elements: 3612
number of nodes: 2046
projection: UTM-33
items:
0: Surface elevation <Surface Elevation> (meter)
1: Total water depth <Water Depth> (meter)
2: U velocity <u velocity component> (meter per sec)
3: V velocity <v velocity component> (meter per sec)
time: 2018-03-07 00:00:00 - 2018-03-11 00:00:00 (5 records)
ds = dfs.read(items="Surface elevation")
ds
<mikeio.Dataset>
dims: (time:5, element:3612)
time: 2018-03-07 00:00:00 - 2018-03-11 00:00:00 (5 records)
geometry: Dfsu2D (3612 elements, 2046 nodes)
items:
0: Surface elevation <Surface Elevation> (meter)
maxwl = ds["Surface elevation"].max(axis=0).values
maxwl.shape
(3612,)
shp = dfs.geometry.to_shapely()
type(shp)
shapely.geometry.multipolygon.MultiPolygon
poly_list = [p for p in shp.geoms]
gdf = gpd.GeoDataFrame({'waterlevel': maxwl},geometry=poly_list, crs=dfs.geometry.projection_string)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
CRSError Traceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[6], line 1
----> 1 gdf = gpd.GeoDataFrame({'waterlevel': maxwl},geometry=poly_list, crs=dfs.geometry.projection_string)
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.13.11/x64/lib/python3.13/site-packages/geopandas/geodataframe.py:243, in GeoDataFrame.__init__(self, data, geometry, crs, *args, **kwargs)
235 if isinstance(geometry, pd.Series) and geometry.name not in (
236 "geometry",
237 None,
238 ):
239 # __init__ always creates geometry col named "geometry"
240 # rename as `set_geometry` respects the given series name
241 geometry = geometry.rename("geometry")
--> 243 self.set_geometry(geometry, inplace=True, crs=crs)
245 if geometry is None and crs:
246 raise ValueError(
247 "Assigning CRS to a GeoDataFrame without a geometry column is not "
248 "supported. Supply geometry using the 'geometry=' keyword argument, "
249 "or by providing a DataFrame with column name 'geometry'",
250 )
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.13.11/x64/lib/python3.13/site-packages/geopandas/geodataframe.py:464, in GeoDataFrame.set_geometry(self, col, drop, inplace, crs)
461 crs = getattr(level, "crs", None)
463 # Check that we are using a listlike of geometries
--> 464 level = _ensure_geometry(level, crs=crs)
465 # ensure_geometry only sets crs on level if it has crs==None
466 if isinstance(level, GeoSeries):
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.13.11/x64/lib/python3.13/site-packages/geopandas/geodataframe.py:71, in _ensure_geometry(data, crs)
69 return GeoSeries(out, index=data.index, name=data.name)
70 else:
---> 71 out = from_shapely(data, crs=crs)
72 return out
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.13.11/x64/lib/python3.13/site-packages/geopandas/array.py:190, in from_shapely(data, crs)
187 raise TypeError(f"Input must be valid geometry objects: {geom}")
188 arr = np.array(out, dtype=object)
--> 190 return GeometryArray(arr, crs=crs)
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.13.11/x64/lib/python3.13/site-packages/geopandas/array.py:340, in GeometryArray.__init__(self, data, crs)
337 self._data = data
339 self._crs = None
--> 340 self.crs = crs
341 self._sindex = None
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.13.11/x64/lib/python3.13/site-packages/geopandas/array.py:391, in GeometryArray.crs(self, value)
388 if HAS_PYPROJ:
389 from pyproj import CRS
--> 391 self._crs = None if not value else CRS.from_user_input(value)
392 else:
393 if value is not None:
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.13.11/x64/lib/python3.13/site-packages/pyproj/crs/crs.py:503, in CRS.from_user_input(cls, value, **kwargs)
501 if isinstance(value, cls):
502 return value
--> 503 return cls(value, **kwargs)
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.13.11/x64/lib/python3.13/site-packages/pyproj/crs/crs.py:350, in CRS.__init__(self, projparams, **kwargs)
348 self._local.crs = projparams
349 else:
--> 350 self._local.crs = _CRS(self.srs)
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.13.11/x64/lib/python3.13/site-packages/pyproj/_crs.pyx:2364, in pyproj._crs._CRS.__init__()
CRSError: Invalid projection: UTM-33: (Internal Proj Error: proj_create: several objects matching this name: Schwarzeck / UTM zone 33S, RGRDC 2005 / UTM zone 33S, Malongo 1987 / UTM zone 33S, ETRS89/DREF91/2016 / UTM zone 33N, ETRS89/DREF91/2016 / UTM zone 33N (N-zE), ETRS89/DREF91/2016 / UTM zone 33N (zE-N))
Ouch… The short and smart projection string “UTM-33” is apparently not understood by GeoPandas. Better look it up on the web https://spatialreference.org/ref/epsg/32433/
gdf = gpd.GeoDataFrame({'waterlevel': maxwl}, geometry=poly_list, crs="EPSG:32433")
gdf.head()
| waterlevel | geometry | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.321391 | POLYGON ((353122.611 6199631.339, 354250.947 6... |
| 1 | 0.254802 | POLYGON ((356811.295 6165979.11, 356926.413 61... |
| 2 | 0.210542 | POLYGON ((334193.183 6143454.831, 332951.036 6... |
| 3 | 0.213418 | POLYGON ((330871.279 6142677.275, 331831.835 6... |
| 4 | 0.208291 | POLYGON ((334327.062 6140906.232, 335381.131 6... |
Export as ESRI Shapefile
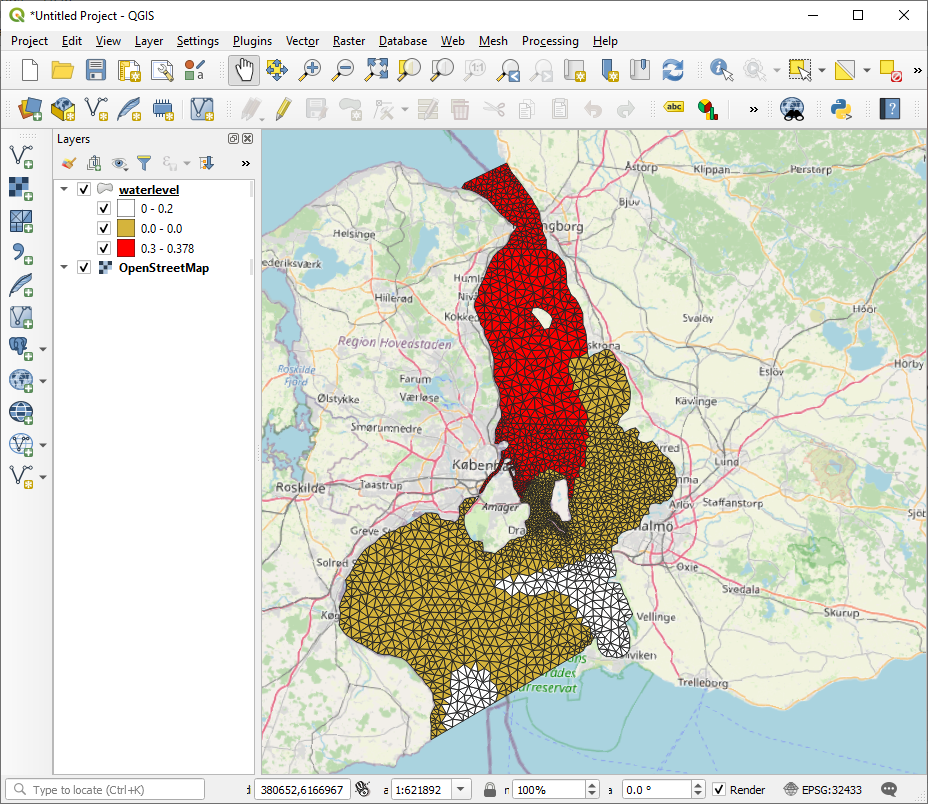
gdf.to_file("waterlevel_utm.shp")
Which can be used together with other data sources and customized in QGIS
Or GeoJSON, which some might prefer…
gdf.to_file("waterlevel_utm.json")